| CPC G01C 21/206 (2013.01) [G01V 3/08 (2013.01); G06F 18/2148 (2023.01); G06F 18/24 (2023.01); G06N 3/02 (2013.01)] | 26 Claims |
|
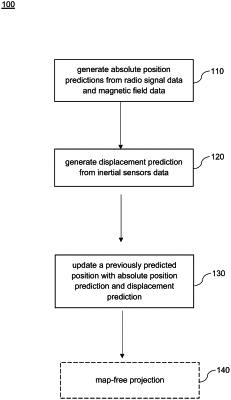
1. A computer-implemented method of determining a position of a portable electronic device in an indoor environment, the method comprising:
at a first rate, updating an absolute position of a portable electronic device within the indoor environment based on at least one of radio signal data and magnetic field data captured using the portable electronic device;
at a second rate that is different than the first rate, selectively updating an estimated displacement of the portable electronic device within the indoor environment, the updating the estimated displacement comprising generating an estimated displacement, by a neural network module, based on inertial sensor data of the portable electronic device; and
determining a present position of the portable electronic device within the indoor environment by updating a previous position based on at least one of (a) the estimated displacement and (b) the absolute position.
|