| CPC F28D 15/0275 (2013.01) [F28D 15/04 (2013.01); H01H 1/62 (2013.01); H01H 9/52 (2013.01); H02B 1/56 (2013.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
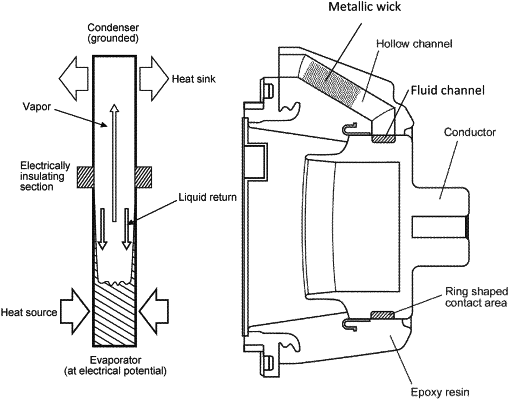
1. A cooling apparatus for a medium voltage or high voltage switchgear, the cooling apparatus comprising:
an evaporator section;
a fluid conduit; and
a condenser section,
wherein, the evaporator section comprises epoxy that completely surrounds a current carrying contact to provide electrical insulation,
wherein, the fluid conduit fluidly connects the evaporator section to the condenser section,
wherein, a section of the fluid conduit is formed and entirely enclosed within the evaporator section around the current carrying contact, and is electrically insulating by the epoxy,
wherein, the cooling apparatus is configured such that, in use, a working fluid in the evaporator section is heated to a vapour state by direct physical contact with the current carrying conductor, and wherein the vapour is transferred by the fluid conduit to the condenser section, and wherein the vapour in the condenser section is condensed to the working fluid, and wherein the condensed working fluid is passively returned via the fluid conduit to the evaporator section, and
wherein the section of the fluid conduit formed within the evaporator section is configured to direct at least a portion of the working fluid into direct physical contact with an outer surface of the current carrying contact.
|