| CPC F25J 1/0022 (2013.01) [F25J 1/0032 (2013.01); F25J 1/005 (2013.01); F25J 1/007 (2013.01); F25J 1/008 (2013.01); F25J 1/0254 (2013.01); F25J 3/0214 (2013.01); F25J 2210/06 (2013.01); F25J 2210/60 (2013.01); F25J 2215/04 (2013.01); F25J 2220/66 (2013.01); F25J 2260/02 (2013.01); F25J 2270/04 (2013.01); F25J 2270/14 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
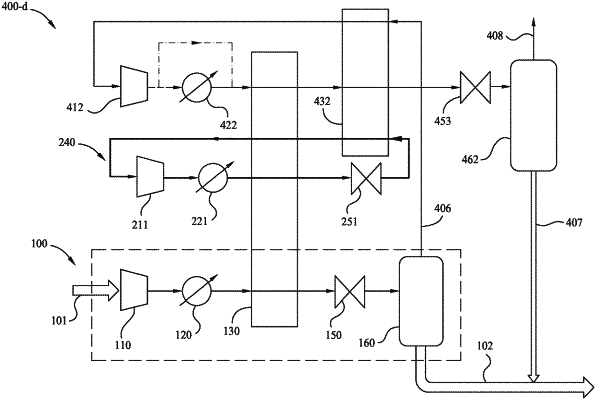
1. A method, comprising:
compressing an input fluid stream comprising at least natural gas and carbon dioxide to generate a first intermediary fluid stream;
cooling the first intermediary fluid stream with a first heat exchanger to generate a second intermediary fluid stream, wherein a temperature of the second intermediary fluid stream is higher than a carbon dioxide-freezing temperature for the second intermediary fluid stream;
expanding the second intermediary fluid stream to generate a third intermediary fluid stream, wherein the third intermediary fluid stream is introduced directly to a separator and the third intermediary fluid stream comprises solid carbon dioxide and a pressure of the third intermediary fluid stream is lower than that of the second intermediary fluid stream;
separating the third intermediary fluid stream in the separator to produce a fourth intermediary fluid stream and a first output fluid stream, wherein the first output fluid stream comprises a slurry of liquefied natural gas (LNG) liquid and the solid carbon dioxide, and the fourth intermediary fluid stream is a gaseous stream;
utilizing the fourth intermediary fluid stream as a cooling fluid stream for a second heat exchanger, thereby generating a fifth intermediary fluid stream;
wherein the fourth intermediary fluid stream is introduced directly to the second heat exchanger;
compressing the fifth intermediary fluid stream to generate a sixth intermediary fluid stream;
cooling the sixth intermediary fluid stream within the first heat exchanger followed by further cooling within the second heat exchanger to generate a seventh intermediary fluid stream, wherein a temperature of the seventh intermediary fluid stream is higher than a carbon dioxide-freezing temperature for the seventh intermediary fluid stream;
expanding the seventh intermediary fluid stream to generate an eighth intermediary fluid stream, wherein the eighth intermediary fluid stream comprises solid carbon dioxide;
separating a second output fluid stream from the eighth intermediary fluid stream, wherein the second output fluid stream comprises a second portion of LNG liquid; and
combining the first output fluid stream with the second output fluid stream to form a combined output fluid stream;
wherein the combined output fluid stream is obtained in an amount that is at least about 85% of a mass input of the input fluid stream.
|