| CPC C25D 9/08 (2013.01) [C23C 28/32 (2013.01); C25D 9/06 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. A method of producing a surface-treated steel sheet, comprising:
subjecting a steel sheet having an Sn coating or an Sn plating layer on at least one side to an anodic electrolytic treatment in an alkaline aqueous solution to form an Sn oxide layer on the Sn coating or the Sn plating layer; and
then subjecting the steel sheet to a cathodic electrolytic treatment in an aqueous solution containing zirconium ions to form a layer containing zirconium oxide on the Sn oxide layer, wherein
the Sn coating or the Sn plating layer has an Sn coating weight of 0.1 g/m2 to 20.0 g/m2 per one side of the steel sheet,
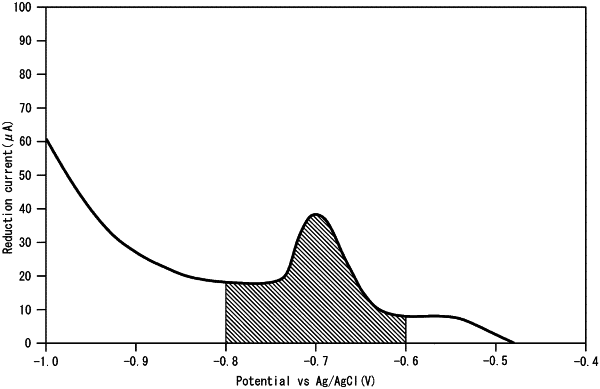
the Sn oxide layer has, at a point in time when the Sn oxide layer is formed, a reduction current peak within a potential range of −800 mV to −600 mV vs. a saturated KCl-Ag/AgCl reference electrode in a current-potential curve obtained by sweeping potential from an immersion potential toward lower potential at a sweeping speed of 1 mV/sec in an aqueous 0.001 N hydrogen bromide solution at 25° C. purged with an inert gas, and an electric quantity of a reduction current in the potential range of 1.5 mC/cm2 to 10.0 mC/cm2, and
the layer containing zirconium oxide has a Zr coating weight of 0.1 mg/m2 to 50.0 mg/m2 per one side of the steel sheet.
|