| CPC B60G 17/0525 (2013.01) [B60G 17/06 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
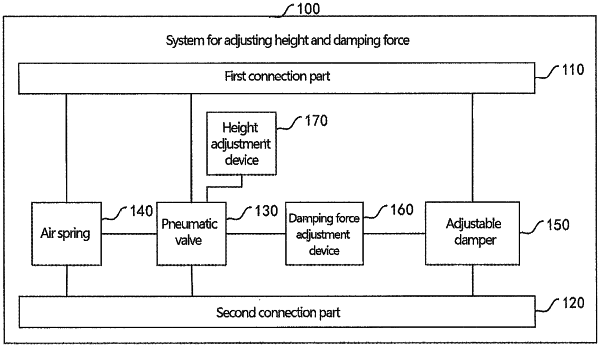
|
1. A method for adjusting height and damping force, comprising:
arranging a pneumatic valve, an air spring, an adjustable damper and a damping force adjustment device configured to adjust the damping force of the adjustable damper between a first connection part and a second connection part, wherein the positions of the pneumatic valve, the air spring, the adjustable damper and the damping force adjustment device fit with each other, and the pneumatic valve is connected to the damping force adjustment device and the air spring respectively;
collecting, by the pneumatic valve, at least one movement variable of the first connection part relative to the second connection part; and
controlling, by the pneumatic valve, the air spring to inflate or deflate according to at least one of the collected movement variable and change in the movement variable, so as to realize height adjustment; and/or carrying out gas driving on the damping force adjustment device to control the adjustable damper to output corresponding damping force, so as to realize adjustment of size of the damping force of the adjustable damper;
wherein the movement variable comprises a positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part, and the positional relationship includes at least one of a vertical relationship and a horizontal relationship;
the positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part being a target value for adjustment, the positional relationship being provided by a total working stroke of the pneumatic valve, and the total working stroke including a total working stroke balance position and at least three displacement threshold ranges, wherein a second displacement threshold range contains a first displacement threshold range, and a third displacement threshold range contains the second displacement threshold range;
the positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part being within the first displacement threshold range, the pneumatic valve neither controlling the air spring to inflate or deflate nor carrying out the gas driving on the damping force adjustment device to control the adjustable damper to output a corresponding damping force, and the damping force of the adjustable damper being a preset basic damping force;
the positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part being between the first displacement threshold range and the second displacement threshold range, the pneumatic valve controlling the air spring to inflate or deflate, but not carrying out the gas driving on the damping force adjustment device to control the adjustable damper to output a corresponding damping force, and the damping force of the adjustable damper being a preset damping force;
the positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part being between the second displacement threshold range and the third displacement threshold range, the pneumatic valve controlling the air spring to inflate or deflate and meanwhile carrying out the gas driving on the damping force adjustment device to control the adjustable damper to output a first damping force, and the first damping force changing with the change of displacement;
the positional relationship of the first connection part relative to the second connection part exceeding the third displacement threshold range, and the pneumatic valve controlling the air spring to inflate or deflate and meanwhile carrying out the gas driving on the damping force adjustment device to control the adjustable damper to output a second damping force;
wherein the second damping force is a damping force corresponding to an terminal impact protection coefficient, and the first damping force is between the preset basic damping force and the second damping force.
|