| CPC B25J 13/089 (2013.01) [B25J 9/1664 (2013.01); B25J 19/023 (2013.01); G01C 21/1656 (2020.08); G05D 1/0251 (2013.01); G05D 1/0253 (2013.01); G05D 1/027 (2013.01); G05D 1/0272 (2013.01); G06V 20/46 (2022.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. An information processing apparatus, comprising:
a first sensor unit configured to periodically sense internal world information associated with an autonomous mobile object to output a plurality of first sensing results;
a second sensor unit configured to sense external world information associated with the autonomous mobile object to output a second sensing result;
a storage configured to store:
a plurality of key frames obtained by previously capturing images at multiple locations in a real space; and
positional information of the multiple locations in association with the plurality of key frames; and
a controller configured to:
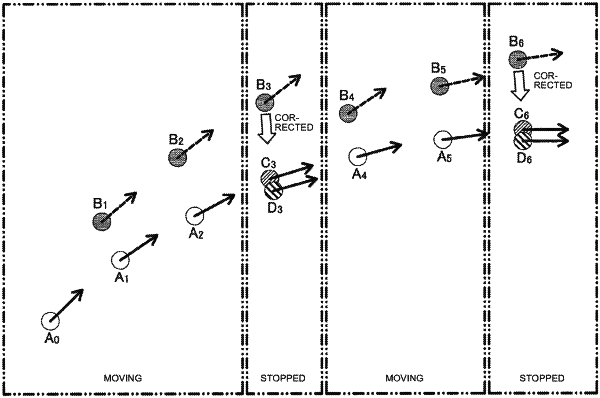
determine a state of the autonomous mobile object is one of a stopped state or a moving state;
determine, based on the determination that the state of the autonomous mobile object is the moving state, that a first estimation method is to be used by the autonomous mobile object for an estimation of a self-position of the autonomous mobile object;
determine, based on the determination that the state of the autonomous mobile object is the stopped state, that a second estimation method is to be used by the autonomous mobile object for the estimation of the self-position of the autonomous mobile object;
periodically estimate, by the first estimation method, the self-position by a periodic integration of the plurality of first sensing results that corresponds to a plurality of first timings until a current time;
estimate, by the second estimation method, the self-position based on the second sensing result, and the positional information of the multiple locations in association with the plurality of key frames;
successively specify, at a first timing of the plurality of first timings when the first sensor unit acquires a first sensing result of the plurality of first sensing results while the state of the autonomous mobile object is the moving state, a condition of a ground on which the autonomous mobile object is moving based on the first sensing result acquired at the first timing;
change, at the first timing, a length of a given distance based on the specified condition of the ground; and
plan a stop condition such that the state of the autonomous mobile object is sequentially changed from the moving state to the stopped state,
wherein the stop condition is planned based on a continuous movement of the autonomous mobile object by the given distance.
|