| CPC H04W 12/122 (2021.01) [H04W 12/63 (2021.01); H04W 64/003 (2013.01); H04W 88/08 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
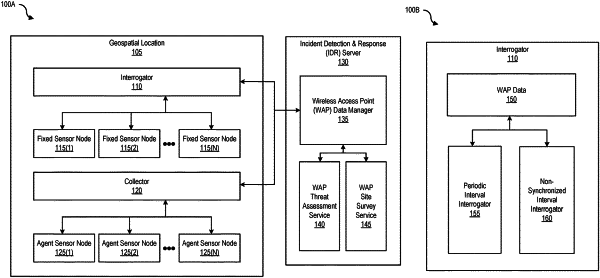
receiving wireless access point (WAP) data associated with a WAP that is implemented in a network at a geospatial location and comprises at least a Service Set Identifier (SSID) and a Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID);
accessing a set of trusted WAPs in the geospatial location that are part of the network;
determining that the SSID of the WAP matches a trusted SSID of at least one trusted WAP of the set of trusted WAPs but the BSSID of the WAP does not match a trusted BSSID of any of the WAPs in the set of trusted WAPs;
determining an approximate location of the WAP in the geospatial location based on a wireless site survey;
generating an alert identifying the approximate location of the WAP in a floor plan visualization of the wireless site survey; and
modifying placement in the geospatial location of one or more trusted WAPs of the set of trusted WAPs.
|