| CPC H03G 3/32 (2013.01) [H04R 5/04 (2013.01); H04R 2430/01 (2013.01)] | 30 Claims |
|
1. A method for automatically controlling loudness of an audio signal to be replayed within a vehicle, the method comprising
an automatic loudness measurer measuring a loudness of an incoming audio signal that comprises a sequence of digital audio blocks;
receiving a noise level indication signal indicating a noise level within the vehicle;
a processor calculating a gain factor based on the measured loudness of the incoming audio signal and the noise level indication signal either using a first type of interpolation or a second type of interpolation, wherein
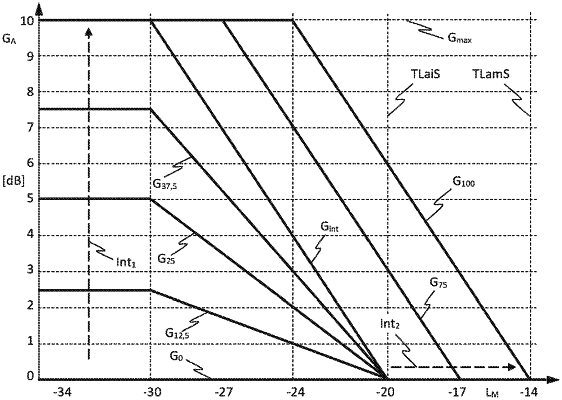
if the measured loudness is equal to or above a predefined first target loudness (TLamS), the gain factor is zero dB;
and otherwise, if the noise level indication signal indicates a noise level equal to or above a predefined intermediate noise level, the second type of interpolation is used, wherein the gain factor is a difference between the measured loudness and a current target loudness, limited to a maximum gain, wherein the maximum gain is a defined absolute maximum gain, and the current target loudness is linearly interpolated, according to the noise level indication signal, between a predefined second target loudness (TLaiS) for the noise level being equal to said intermediate noise level and the predefined first target loudness (TLamS) for the noise level being equal to a predefined maximum noise level;
and otherwise, if the noise level indication signal indicates a noise level below the intermediate noise level, the first type of interpolation is used, wherein the gain is linearly interpolated, according to the noise level, between the gain as defined for the intermediate noise level and zero; and
applying the gain factor to the audio signal to be replayed.
|