| CPC G06N 5/04 (2013.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 17/18 (2013.01)] | 9 Claims |
|
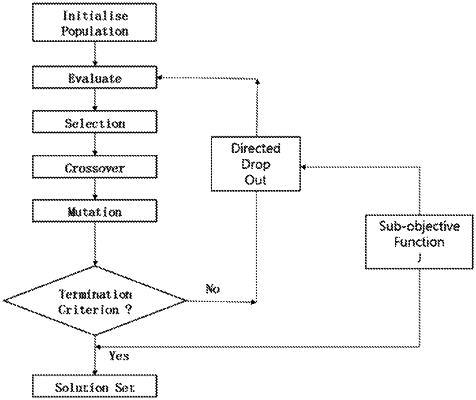
1. An optimization calculation apparatus comprising:
an algorithm module obtaining a plurality of first solutions (S1) from a plurality of input data, obtaining second solutions (S2) from the first solutions (S1) and repeating the process to derive an optimal solution (Sm); and
a similarity determination module connected to the algorithm module and computing a similarity of ith solutions in order to obtain (i+1)th solutions (1≤i≤m−1),
wherein, in the algorithm module, the ith solutions are clustered according to the similarity computed by the similarity determination module and arbitrary solutions are selected from the clustered ith solutions to obtain the (i+1)th solutions, and
wherein the similarity is computed by using a similarity determination function in the similarity determination module, and the similarity determination function uses a reference vector (Oi) representing a center of gravity of (i−1)th solution vectors, a radius (ri,jk, ri,jl) between the reference vector and the ith solution vectors, an adjacent distance (di,jk,jl) between two different ith solution vectors and an angle (θi,jk,jl) between the two solution vectors based on the reference vector.
|