| CPC G06F 21/32 (2013.01) [G06F 21/34 (2013.01); G06V 40/45 (2022.01); G06V 40/70 (2022.01); G10L 17/00 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
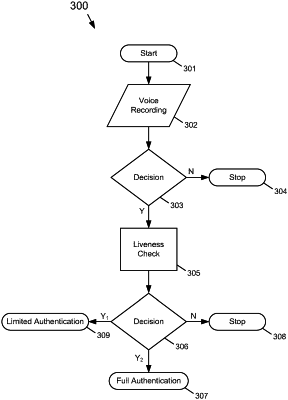
1. A method to authenticate a user of a computing device, the method comprising:
presenting a plurality of audible cues to the user through an audio output device of the computing device;
requiring, by the computing device, the user to orally respond to the plurality of cues in an interactive manner;
obtaining from a first sensor coupled to the computing device a first representation of a liveness characteristic of the user, wherein the first representation is an audio representation of the interactive oral responses of the user to the plurality of audible cues indicating that the user is alive and wherein the first sensor comprises an audio input device that captures the audio representation;
comparing by an authentication processor of the computing device the first representation of the liveness characteristic of the user to a second representation of the liveness characteristic of the user, the second representation of the liveness characteristic of the user comprising at least a portion of a dialog spoken by the user that was obtained prior to the first representation of the liveness characteristic of the user;
determining by the authentication processor whether a level of stress of the user contained in the first representation of the liveness characteristic of the user is greater than a level of stress of the user contained in the second representation of the liveness characteristic of the user; and
disabling by the authentication processor a first predetermined level of access to the computing device based on the level of stress of the user contained in the first representation of the liveness characteristic of the user being an increased level of stress compared to the second representation of the liveness characteristic of the user.
|