| CPC G01R 33/5608 (2013.01) [G01R 33/5602 (2013.01); G06T 3/4084 (2013.01); G16H 30/40 (2018.01)] | 8 Claims |
|
1. A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus comprising,
a measuring unit having a transmission unit configured to transmit an RF magnetic field pulse to a subject disposed in a static magnetic field;
a receiving unit configured to receive a nuclear magnetic resonance signal generated by the subject;
a gradient magnetic field generator for providing a gradient magnetic field to the static magnetic field; and
a computer configured to perform an operation on the nuclear magnetic resonance signal received by the receiving unit,
wherein the computer is programmed to:
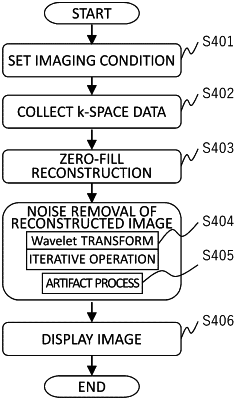
process the nuclear magnetic resonance signal being received to generate a reconstructed image with a reconstruction matrix obtained by extending an acquisition matrix by zero-filling,
remove noise from the reconstructed image after changing the size of a matrix of the reconstructed image by setting a mother wavelet as a reference and expanding/contracting and parallel translating the mother wavelet, thereby creating a noise-removed image,
restore the matrix of the reconstructed image after the noise removal, to the reconstruction matrix,
convert the noise-removed image from the image space data to k-space data by a Fourier transform, and
cut out a reconstruction matrix size that is a same as a size prior the extending of the acquisition matrix in the k-space to obtain the reconstructed image.
|