| CPC F16H 15/38 (2013.01) [B64D 41/00 (2013.01); F16H 57/042 (2013.01); F16H 57/049 (2013.01); H02K 7/116 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A toroidal continuously variable transmission comprising:
input and output discs opposed to each other;
a power roller tiltably held between the input and output discs to transmit rotational drive power of the input disc to the output disc at a speed ratio determined by a tilt angle of the power roller; and
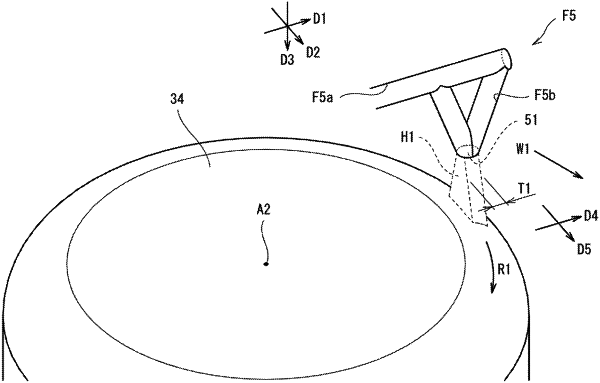
a discharge structure including an outlet that discharges an oil, wherein
the discharge structure includes first and second oil passages connected with each other inside the discharge structure, and
the first and second oil passages are arranged such that the oil flowing through the first oil passage and the oil flowing through the second oil passage collide with each other in the vicinity of the outlet and that a jet of oil discharged from the outlet forms a flattened shape extending along a rotational direction of the power roller.
|