| CPC C12Q 1/6806 (2013.01) [C40B 20/08 (2013.01); C40B 30/10 (2013.01); C40B 60/06 (2013.01); G16B 40/10 (2019.02); G16B 30/00 (2019.02)] | 2 Claims |
|
1. A method comprising:
(a) isolating DNA from a source, thereby providing a composition comprising the isolated DNA, wherein the isolated DNA has at least a first target region having a first length in nucleotides and a second target region having a second length in nucleotides, wherein the second length is greater than the first length, and the first target region and the second target region are a long interspersed nuclear element (LINE);
(b) quantifying a total mass of the isolated DNA in the composition;
(c) quantifying a first concentration of the first target region and a second concentration of the second target region in the composition;
(d) calculating a Q-ratio for the isolated DNA by dividing the second concentration by the first concentration;
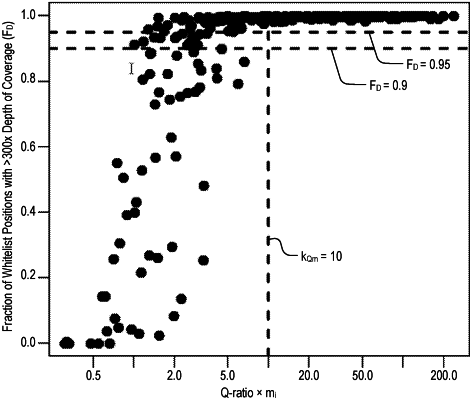
(e) determining a value for a quality-mass constant (kQm) by a method comprising: (i) sequencing a plurality of regions of a plurality of isolated DNA samples, wherein each of the isolated DNA samples has a known input mass and a known Q-ratio; (ii) comparing a fraction (FD) of the plurality of the regions with a selected depth of coverage as determined by sequencing in step (a) with a product of the input mass and the Q-ratio for each of the isolated DNA samples; (iii) identifying a minimum value for the product of the input mass and the Q-ratio at which FD is greater than a target FD; and (iv) setting the quality-mass constant (kQm) equal to the minimum value for the product of the input mass and the Q-ratio determined in step (iii);
(f) estimating a required input mass for the isolated DNA by dividing the quality-mass constant (kQm) by the Q-ratio; and
(g) preparing the isolated DNA for sequencing if the total mass of the isolated DNA in the composition is equal or greater than the required input mass.
|