| CPC A61C 9/0053 (2013.01) [A61B 1/000094 (2022.02); A61B 1/000096 (2022.02); A61B 1/00172 (2013.01); A61B 1/00186 (2013.01); A61B 1/00194 (2022.02); A61B 1/0638 (2013.01); A61B 1/0646 (2013.01); A61B 1/24 (2013.01); A61B 5/0086 (2013.01); A61B 5/0088 (2013.01); A61B 6/145 (2013.01); A61C 7/002 (2013.01); A61C 13/0004 (2013.01); G06T 19/00 (2013.01); A61B 5/0062 (2013.01); A61B 5/0066 (2013.01); A61B 5/4547 (2013.01); A61C 13/0019 (2013.01); A61C 13/34 (2013.01); G06T 2200/24 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30036 (2013.01); G06T 2210/41 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
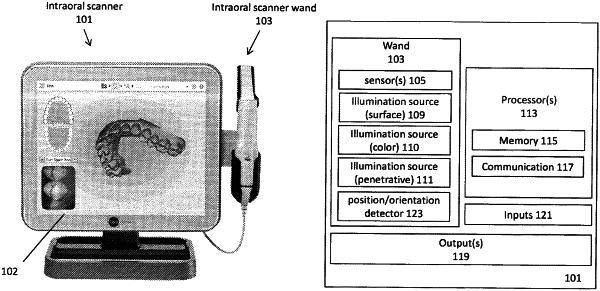
1. An intraoral scanning system, the system comprising:
a wand having at least one image sensor and a near-infrared (near-IR) light source; and
one or more processors operably connected to the wand, the one or more processors configured to:
display a three-dimensional (3D) model of a patient's dental arch;
display a viewing window over a portion of the 3D model of the patient's dental arch;
change a relative position between the viewing window and the 3D model of the patient's dental arch based on input from the user;
identify, from a plurality of near-IR images of the patient's dental arch that were taken from different angles and positions relative to the patient's dental arch, an identified near-IR image taken at an angle and position that approximates a relative angle and position between the viewing window and the 3D model of the patient's dental arch; and
display the identified near-IR image taken at the angle and position that approximates the relative angle and position between the viewing window and the 3D model of the patient's dental arch.
|