| CPC A61B 6/5282 (2013.01) [A61B 6/4266 (2013.01); A61B 6/4291 (2013.01); A61B 6/461 (2013.01); A61B 6/483 (2013.01); A61B 6/505 (2013.01); A61B 6/5205 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
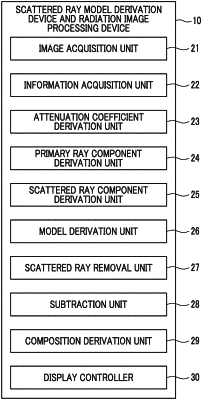
1. A scattered ray model derivation device comprising:
at least one processor,
wherein the processor
acquires at least one standard image representing a standard object having different thicknesses, the at least one standard image being obtained by imaging the standard object by radiation in a state in which an object is interposed between the standard object and a radiation detector,
derives a relationship between the thickness of the standard object and a radiation attenuation coefficient of the standard object, which corresponds to an energy characteristic of the radiation, the relationship reflecting an influence of beam hardening by the standard object and the object,
derives a primary ray component corresponding to the thickness of the standard object included in the standard image based on the relationship between the thickness of the standard object and the radiation attenuation coefficient of the standard object,
derives a scattered ray component corresponding to the thickness of the standard object included in the standard image based on a difference between the standard image and the primary ray component, and
derives a scattered ray model representing a relationship between the thickness of the standard object and a ratio of the scattered ray component to the primary ray component.
|