| CPC A61B 5/0261 (2013.01) [A61B 1/041 (2013.01); A61B 3/12 (2013.01); A61B 3/1241 (2013.01); A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/489 (2013.01); A61B 5/0077 (2013.01); A61B 5/0084 (2013.01); F04C 2270/041 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
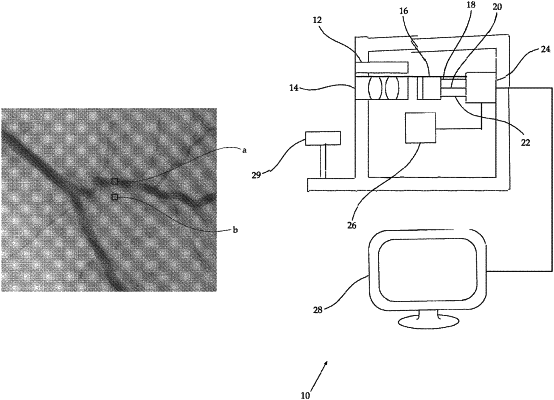
1. A method for in vivo imaging of blood vessels, the method comprising:
selecting a first wavelength range of light corresponding to a certain reflectance spectrum of a blood-containing region and higher absorbance in blood than non-blood bodily tissue;
illuminating an area of interest of a surface with light comprising wavelengths within the first wavelength range, said first wavelength range including predominantly light having wavelengths of between 400 nm and 620 nm;
acquiring a first pixelated image of light reflected from said area of interest of the surface at said first wavelength range of light;
selecting a second wavelength range of light corresponding to a certain reflectance spectrum of a region devoid of blood and absorbance in blood similar to that of non-blood bodily tissue;
illuminating said area of interest of the surface with light comprising wavelengths within the second wavelength range, said second wavelength range including predominantly light having wavelengths of between 620 nm and 800 nm; wherein said illuminating with light comprising wavelengths within said first wavelength range is performed simultaneously with said illuminating with light comprising wavelengths within said second wavelength range; wherein said illuminating is with light having at least two discrete wavelengths of light: at least one discrete wavelength within said first wavelength range and at least one discrete wavelength within said second wavelength range; wherein said illuminating comprises illuminating with incoherent light;
directing light collected for acquiring said first image and said second image from said area of interest to a single image-acquirer;
separating data acquired by said single image-acquirer constituting said first image from data acquired by said single image-acquirer constituting said second image;
acquiring a second pixelated image of light reflected from said area of interest of the surface at said second wavelength range of light;
generating by a processor a first image of an area of interest including at least one blood-containing feature of a surface of said first wavelength range corresponding to a certain reflectance spectra of a blood-containing region;
generating by a processor a second image of an area of interest of a surface of a second wavelength range, being different from said first wavelength and corresponding to a certain reflectance spectra of a region devoid of blood; and
generating by a processor a monochromatic image of at least one blood-containing feature by processing only said first image and said second image, by for each desired location i of said area of interest, identifying a corresponding pixel P1(i) in said first image and a corresponding pixel P2(i) in said second image; and calculating a pixel P3(i) in said monochromatic image corresponding to said location i, by dividing pixels of the first and second images P1(i) by P2(i) or P2(i) by P1(i), wherein the monochromatic image has at least one of increased contrast between the blood-containing feature and adjacent tissue and increased spatial resolution at the border between the blood-containing feature and adjacent tissue as compared with the first and second images.
|