| CPC H10N 60/0884 (2023.02) [G06N 10/00 (2019.01); H10N 60/0661 (2023.02); H10N 60/0912 (2023.02); H10N 60/12 (2023.02); H10N 60/805 (2023.02)] | 24 Claims |
|
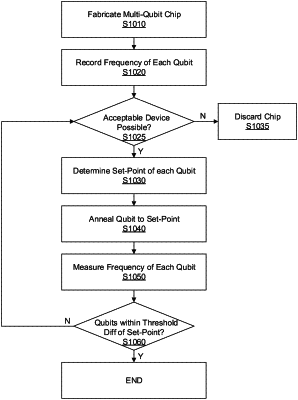
1. A method of forming a multi-qubit chip, the method comprising:
forming a plurality of qubits on a chip, wherein each qubit comprises a Josephson junction and a capacitor connected in parallel with one another;
measuring a resonance frequency of each qubit on the chip;
determining a set-point frequency for each qubit that achieves a defined collision probability with respect to a probability of frequency collisions between adjacent qubits; and
annealing a first Josephson junction of a first qubit of the plurality of qubits using a laser, based on parameters for the annealing from a database that relates the parameters to frequency shifts, to change the resonance frequency of the first qubit from a first resonance frequency to about a first set-point frequency determined for the first qubit.
|