| CPC H04S 7/30 (2013.01) [H04S 2420/01 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
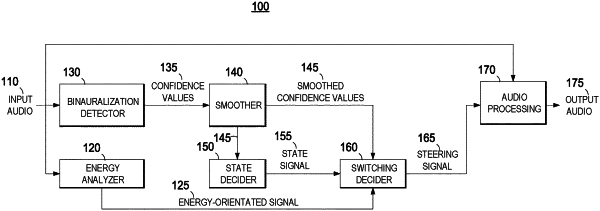
1. A method for steering binauralization of audio, the method comprising steps of:
receiving an audio input signal, the audio input signal comprising a plurality of audio frames;
calculating a confidence value indicating a likelihood that a current audio frame of the audio input signal comprises binauralized audio;
determining a state signal based on the confidence value, the state signal indicating that the current audio frame being in an un-binauralized state or in a binauralized state;
determining a steering signal, wherein, upon the state signal being changed from indicating the un-binauralized state to indicating the binauralized state:
changing the steering signal to activate binauralization of audio by applying a head related transfer function, HRTF, on the audio input signal resulting in a binauralized audio signal, and
generating an audio output signal, at least partly comprising the binauralized audio signal;
wherein, upon the state signal being changed from indicating the binauralized state to indicating the un-binauralized state, setting a deactivation mode of binauralization to true; and
upon the deactivation mode of the binauralization being true, and the confidence value of the current audio frame being below a deactivation threshold, and an energy value of the current audio frame being lower than energy values of a threshold number of audio frames of the audio input signal previous to the current audio frame:
setting the deactivation mode of the binauralization to false,
changing the steering signal to deactivate or reduce binauralization of audio, and
generating the audio output signal at least partly comprising the audio input signal.
|