| CPC H02K 21/38 (2013.01) [H02K 11/30 (2016.01); H02P 21/14 (2013.01); H02P 21/34 (2016.02); H02P 25/089 (2016.02); H02P 2207/05 (2013.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
1. A sensorless permanent magnet assisted synchronous reluctance motor comprising:
a stator mounted having a three-phase stator winding configuration;
a rotor including a magnetic permeability core having a plurality of flux barriers that divide the core into a plurality of main rotor flux path segments to control flow of magnetic flux within the rotor, wherein the plurality of flux barriers hold a plurality of permanent magnets, the magnetic permeability core including a plurality of surface bridges that join the plurality of rotor flux path segments together, the rotor being rotatable relative to the stator via excitation of the three-phase stator winding configuration of the stator, wherein the plurality of permanent magnets generate a plurality of rotor magnetic poles having magnetic polarity;
a main magnetic flux path between at least one of the plurality of rotor flux path segments and the stator;
an unloaded leakage magnetic flux path through at least one of the plurality of surface bridges having a directionally magnetized flux density caused by at least one of the plurality of permanent magnets;
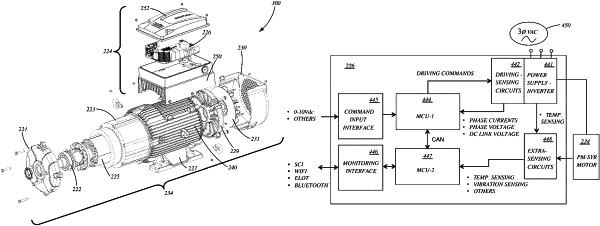
a motor control system including:
a power supply;
a sensing circuit configured to sense one or more electrical characteristics of the stator;
a controller configured to:
apply a positive voltage pulse and a negative voltage pulse to the three-phase stator winding configuration, wherein the magnitude of the positive voltage and the negative voltage pulse are selected such that:
one of the positive voltage pulse and the negative voltage pulse demagnetizes the directionally magnetized flux density in the at least one of the plurality of surface bridges, and
the other one of the positive voltage pulse and the negative voltage pulse further magnetizes the flux density in the at least one of the plurality of surface bridges;
detect a current response to the positive voltage pulse and a current response to the negative voltage pulse;
determine the magnetic polarity of the plurality of magnetic poles based on relative magnitudes of the current response to the positive voltage pulse and the current response to the negative voltage pulse;
generate driving commands during motor startup based on the determined magnetic polarity of the plurality of magnetic poles; and
a driving circuit for generating excitation signals for the three-phase stator winding configuration of the stator according to the driving commands during motor startup.
|