| CPC H01P 1/2002 (2013.01) [H01P 1/2053 (2013.01); H01P 1/225 (2013.01); H01P 7/04 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
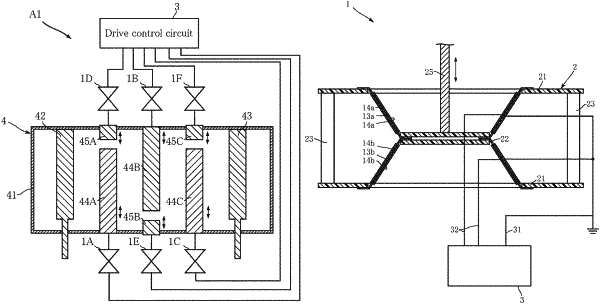
1. A high frequency filter comprising:
a high frequency filter body that includes a metal housing, an input unit, an output unit, a plurality of resonant elements, and a plurality of adjusting elements disposed to face the plurality of resonant elements, respectively;
frequency characteristics such that an amount of attenuation for an input electrical signal is smaller in a first frequency band than in a second frequency band; and
a plurality of dielectric elastomer transducers, each including a dielectric elastomer layer and a pair of electrode layers sandwiching the dielectric elastomer layer,
wherein any one of the dielectric elastomer transducers is configured to vary the frequency characteristics,
wherein the plurality of dielectric elastomer transducers are configured to move the plurality of resonant elements, respectively, relative to the metal housing, and
wherein the plurality of dielectric elastomer transducers are configured to move the plurality of adjusting elements, respectively, relative to the metal housing.
|