| CPC G06N 5/045 (2013.01) [G06N 20/00 (2019.01); G06F 3/0482 (2013.01)] | 7 Claims |
|
1. A system that provides an estimated result using a learning model, the system comprising:
a memory storing instructions; and
a processor that is capable of executing the instructions stored in the memory causing the system to:
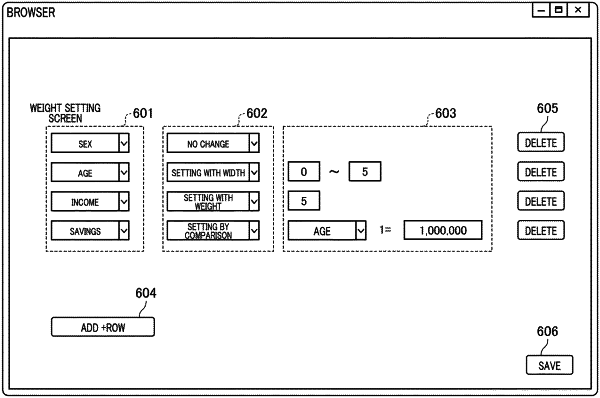
set a condition with regard to at least one parameter among a plurality of parameters, the set condition limiting a change of an input value of the at least one parameter in a case where the input value of the at least one parameter is changeable to change the estimated result provided using the learning model;
execute an estimation using the learning model based on respective input values corresponding to the plurality of parameters; and
provide the estimated result of the executed estimation and information necessary to change the estimated result,
wherein the provided information necessary to change the estimated result indicates a change of the input value of the at least one parameter that will change the estimated result provided using the learning model and that is not limited according to the set condition,
wherein, as the set condition, respective weights for a plurality of category elements of at least one parameter among the plurality of parameters are designated, and the plurality of category elements are used for categorizing a user corresponding to the input values associated with the plurality of parameters, and
wherein the respective weights indicate, in changing the estimated result, comparative easiness of a change of value for another parameter among the plurality of parameters.
|