| CPC G01V 1/282 (2013.01) [G01V 1/362 (2013.01); G01V 2210/512 (2013.01); G01V 2210/67 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
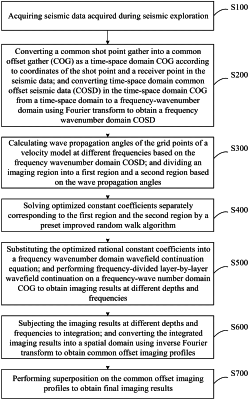
1. A seismic imaging method, comprising:
(S100) collecting seismic data comprising seismic source type, seismic source dominant frequency, location of a shot point, maximum tectonic angle, a set temporal sampling interval, a size of a velocity model, and a spatial interval;
(S200) extracting a common shot point gather from the seismic data; converting the common shot point gather to a time-space domain common offset gather according to the location of the shot point and a location of a receiver point; and converting time-space domain common offset seismic data in the time-space domain common offset gather from time-space domain to frequency-wavenumber domain by using Fourier transform to obtain frequency-wavenumber domain common offset seismic data;
(S300) calculating a plurality of wave propagation angles of a plurality of grid points of the velocity model based on the frequency-wavenumber domain common offset seismic data through the following equation:
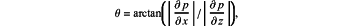 wherein θ represents the wave propagation angles; ∂p/∂x represents a partial derivative of a seismic wavefield in x direction; and ∂p/∂z represents a partial derivative of the seismic wavefield in z direction; and
dividing an imaging region into a first region and a second region based on the plurality of wave propagation angles, wherein a wave propagation angle of the first region is smaller than a wave propagation angle of the second region;
(S400) calculating a plurality of optimized constant coefficients corresponding to the first region and the second region according to the following equation:
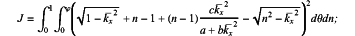 wherein J is an objective function; θ represents the wave propagation angle; n is a medium refractive index; a, b and c represent the plurality of optimized constant coefficients; kx represents wavenumber in x direction; kx represents normalized wavenumber in x direction, and kx=kx/k0; k0 represents wavenumber based on background velocity; and φ is a set maximum imaging angle;
(S500) constructing a rational function-approximation dispersion relation based on heterogeneity of a real underground medium; and substituting the rational function-approximation dispersion relation into a frequency-wavenumber domain Fourier wavefield continuation fundamental equation to obtain a frequency-wavenumber domain wavefield continuation equation, expressed as:
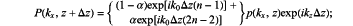 wherein P(kx,z+Δz) represents wavefield information at a depth of z+Δz; kz represents wavenumber in z direction; p(kx,z) represents wavefield information at a depth of z; α is an intermediate parameter variable, represented by
 i represents an imaginary number; and Δz represents a spatial sampling interval along a depth direction; and
substituting the plurality of optimized constant coefficients obtained in step (S400) into the intermediate parameter variable α of the frequency-wavenumber domain wavefield continuation equation, and processing the frequency-wavenumber domain common offset seismic data by using the frequency-wavenumber domain wavefield continuation equation thereby obtaining a plurality of images at different depths and frequencies;
(S600) integrating the plurality of images to obtain a plurality of integrated images; and transforming the plurality of integrated images to a spatial domain by using inverse Fourier transform to obtain a plurality of common offset imaging profiles; and
(S700) superposing the plurality of common offset imaging profiles to obtain a seismic image.
|