| CPC G01J 3/443 (2013.01) [B63B 25/16 (2013.01); B63J 2/14 (2013.01); F02M 21/0215 (2013.01); F17C 6/00 (2013.01); F17C 9/02 (2013.01); F17C 9/04 (2013.01); F17C 2221/033 (2013.01); F17C 2227/0164 (2013.01); F17C 2227/0185 (2013.01); F17C 2227/0339 (2013.01); F17C 2227/0348 (2013.01); F17C 2227/0358 (2013.01); F17C 2265/033 (2013.01); F17C 2265/034 (2013.01); F17C 2265/037 (2013.01); F17C 2265/038 (2013.01); F17C 2265/066 (2013.01); F17C 2270/0105 (2013.01); G01J 2003/423 (2013.01); G01N 21/718 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. A laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) device, the device comprising:
a laser projector configured to project a pulsed beam to a target;
a light receiving module configured to receive a target light, wherein the target light includes a light in connection with plasma ablation induced at the target by the pulsed beam;
a spectrometer optically connected to the light receiving module and configured to obtain a spectrum data related to the target light received from the light receiving module, the spectrometer comprising:
a spectral member for separating light received from the light receiving module; and
sensor arrays configured to detect the separated light from the spectral member in a predetermined wavelength band, wherein the sensor arrays include a plurality of image sensors arranged to measure a plurality of intensities of the separated light corresponding to a plurality of specific wavelength bands included in the predetermined wavelength band,
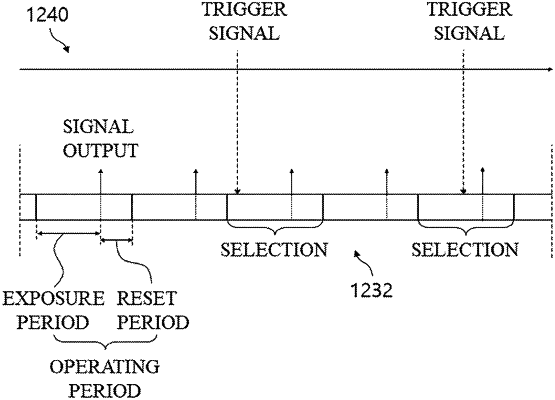
wherein the sensor arrays are configured to alternately and repeatably operate 1) a plurality of exposure periods for accumulating electrical energy according to the detected light and 2) a plurality of reset periods for initializing the electrical energy accumulated during the exposure period and the sensor arrays configured to generate the spectrum data related to the detected light in the exposure period,
wherein the sensor arrays are configured to be set for the exposure period to have a predetermined duration such that the spectrum data related to the target light includes 1) first spectrum information related to the continuum emission having overall intensity values for the predetermined wavelength band and 2) second spectrum information related to the element specific emission having intensity values of one or more spectral peaks within the predetermined wavelength band; and
a controller configured to:
obtain a plurality of spectrum data corresponding to the plurality of exposure periods of the spectrometer,
select a specific exposure period based on an occurrence of the projection of the pulsed beam,
obtain the target spectrum data of the target light generated in connection with the plasma ablation from the selected specific exposure period, and
provide, by using an artificial neural network, diagnostic information on whether the target is related to a disease based on the spectrum data.
|