| CPC F16K 7/16 (2013.01) [F16K 31/007 (2013.01); C23C 16/45544 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
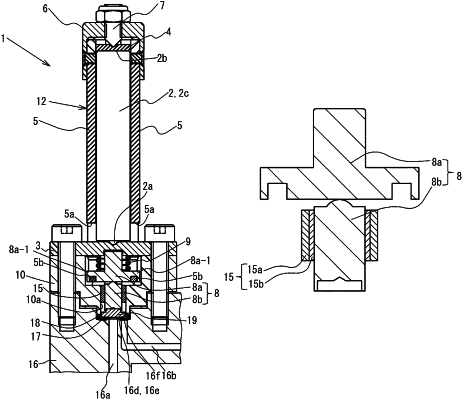
1. A diaphragm valve comprising: a valve body having a flow path formed therein and a valve chamber recessed from an upper surface of the valve body; a diaphragm that is disposed in the valve chamber and elastically deformable to open and close the flow path and adjust an opening degree of the flow path; a stem for pressing the diaphragm to elastically deform the diaphragm; an actuator for driving the stem; and a support that is fixed to the valve body and supports the stem and the actuator;
the stem and the actuator being arranged in series in this order from the upper surface of the valve body in a direction perpendicular to the upper surface,
the actuator being positioned such that a lower end portion abuts on a member of the support and a vertical position of an upper end portion is movable,
the upper end portion of the actuator and the stem being connected via a displacement transmitter extending so as to bypass the actuator,
wherein the stem comprises a first stem member connected to the displacement transmitter, and a second stem member held by the support so as to be movable in an axial direction via a sleeve, the second stem member has an upper end portion which abuts against a lower end portion of the first stem member, and is driven by the first stem member to press the diaphragm, and
wherein the upper end portion of the second stem member is in point contact with the lower end portion of the first stem member.
|