| CPC C02F 9/00 (2013.01) [B01D 61/025 (2013.01); B01D 61/08 (2013.01); B01D 61/10 (2013.01); B04C 5/04 (2013.01); B04C 5/081 (2013.01); B04C 5/085 (2013.01); B04C 5/20 (2013.01); C04B 35/12 (2013.01); C04B 35/62222 (2013.01); B01D 2311/08 (2013.01); B01D 2311/103 (2013.01); B01D 2311/12 (2013.01); B01D 2311/2634 (2013.01); B01D 2311/2642 (2013.01); B01D 2311/2649 (2013.01); B01D 2311/2676 (2013.01); B01D 2313/221 (2022.08); C02F 1/02 (2013.01); C02F 1/38 (2013.01); C02F 1/441 (2013.01); C02F 1/52 (2013.01); C02F 1/72 (2013.01); C02F 2101/36 (2013.01); C02F 2103/06 (2013.01); C02F 2303/10 (2013.01); C04B 2235/9692 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
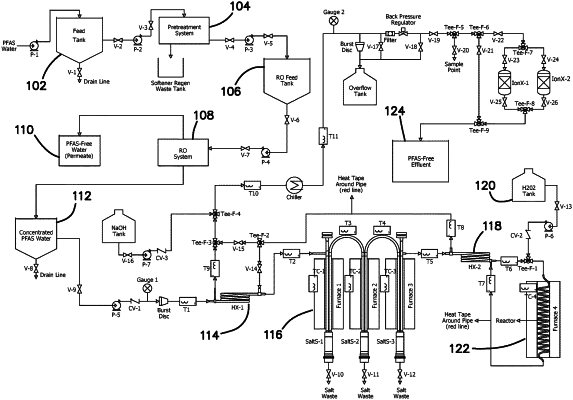
1. A method of destroying PFAS, comprising: providing an aqueous solution comprising water and PFAS;
subjecting the aqueous solution to reverse osmosis to produce a clean water fraction and a briny concentrated fraction in which the PFAS concentration is at least 50% greater than the aqueous solution;
preheating the briny concentrated fraction in a heat exchanger to form a preheated concentrated fraction that is at subcritical conditions;
passing the preheated concentrated fraction into a pre-reactor where the briny concentrated fraction is converted to supercritical conditions at a first temperature causing sodium chloride to precipitate;
removing at least a portion of the sodium chloride to produce a brine-reduced fraction;
passing the brine-reduced fraction to a reactor where the fraction is subjected to oxidation under supercritical conditions wherein the concentration of oxidant and/or temperature is higher than in the pre-reactor;
producing a clean hot water solution having a concentration of PFAS that is at least 90% less than the aqueous solution; and, wherein a fuel or oxidizer is added to the pre-reactor; and further comprising transferring heat from the clean hot water solution to the aqueous solution in the heat exchanger in the preheating step.
|