| CPC A61B 5/245 (2021.01) [A61B 5/067 (2013.01); A61B 5/4839 (2013.01); A61B 5/6803 (2013.01); A61B 5/684 (2013.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0223 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. An inductive sensor apparatus for brain diagnostics comprising:
a first sensor coil connected with a first resistive, inductive, and capacitive (RLC) circuit and first frequency counter;
a second sensor coil connected with a second RLC circuit and second frequency counter, the second sensor coil having a larger or smaller diameter than the first sensor coil, the first and second sensor coils forming a sensor unit;
a memory storing control values derived from prior sensor coil measurements of one or more normal brains in vivo, each control value associated with a corresponding cranial location;
a computer processor operatively connected with a machine-readable non-transitory medium embodying information indicative of instructions for causing the computer processor to perform operations comprising:
generating measure values based on outputs from the first and second frequency counters when the sensor unit is at a cranial location;
determining the cranial location at which the measured values are associated;
retrieving, from the memory, control values associated with the cranial location;
comparing the measured values to the control values to generate deltas;
comparing the deltas to a positive threshold and a negative threshold associated with each cranial location to ascertain an exceedance, the exceedance having a sign and a magnitude; and
outputting an indication based on the sign of the exceedance, and an indicator or display connected with the computer processor for the indications.
|
|
13. A method of diagnosing an issue in a subject's brain, the method comprising:
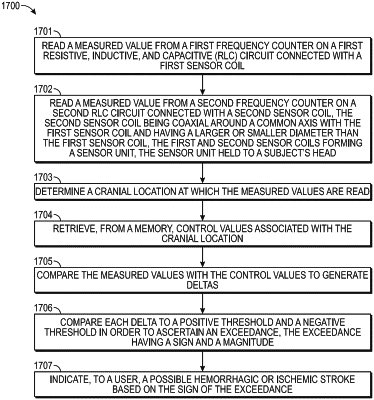
reading a measured value from a first frequency counter on a first resistive, inductive, and capacitive (RLC) circuit connected with a first sensor coil;
reading a measured value from a second frequency counter on a second RLC circuit connected with a second sensor coil, the second sensor coil being coaxial around a common axis with the first sensor coil and having a larger or smaller diameter than the first sensor coil, the first and second sensor coils forming a sensor unit, the sensor unit held to a subject's head;
determining a cranial location at which the measured values are read;
retrieving, from a memory, control values associated with the cranial location;
comparing the measured values with the control values to generate deltas;
comparing each delta to a positive threshold and a negative threshold in order to ascertain an exceedance, the exceedance having a sign and a magnitude; and
indicating, to a user, a type of issue based on the sign of the exceedance.
|