| CPC A61B 5/02042 (2013.01) [A61B 5/02055 (2013.01); A61B 5/4848 (2013.01); A61B 5/6826 (2013.01); A61B 5/6829 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61B 5/7425 (2013.01); A61B 5/026 (2013.01); A61B 5/0531 (2013.01); A61B 5/443 (2013.01); A61B 5/7435 (2013.01); A61B 2505/05 (2013.01); A61B 2562/029 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A noninvasive method for detecting blood volume imbalances in a mammalian subject comprising:
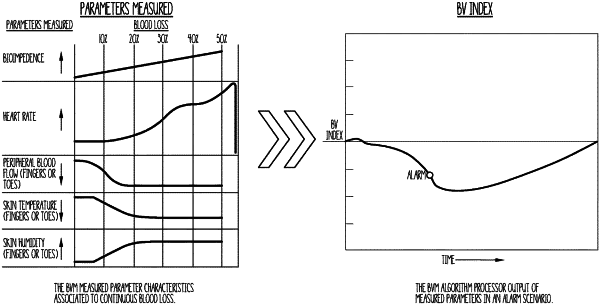
noninvasively obtaining baseline physiologic value measurements, over a period of time from the subject, of at least three of physiological parameters selected from the group including heart rate, electrical body impedance, skin temperature, perfusion index, peripheral blood flow, and skin humidity; and
with at least one integrated circuit:
computing, using the baseline physiologic value measurements, a starting value blood volume index which indicates 100% of the subject's normal total blood volume;
displaying the starting value blood volume index on an electronic display;
after computing said starting value blood volume index, noninvasively obtaining real time physiologic value measurements of the selected at least three physiological parameters;
computing, with an algorithm, a real time blood volume index of the subject based upon difference values calculated between the baseline physiologic value measurements and corresponding real time physiologic value measurements, wherein the algorithm includes coefficients for weighting each difference value used to compute the real time blood volume index;
displaying the real time blood volume index on the electronic display; and
displaying, on the electronic display, changes in the real time blood volume index, from the starting value blood volume index, that indicate blood volume imbalances as low as 10% of the subject's normal total blood volume.
|