| CPC A61B 34/30 (2016.02) [A61B 90/50 (2016.02); G06F 3/017 (2013.01); G06F 3/0444 (2019.05); G06F 3/0446 (2019.05); A61B 2017/00207 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0257 (2013.01); G06F 2203/04108 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A surgical robotic system comprising:
a surgical robotic arm having a plurality of robotic arm links and a plurality of j oints operable to move according to multiple degrees of freedom;
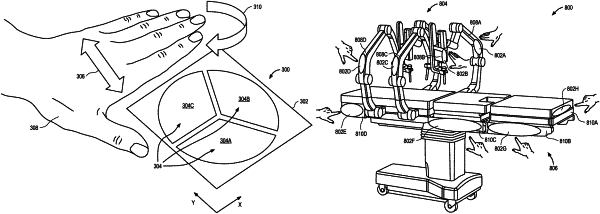
a proximity sensor coupled to the surgical robotic arm, the proximity sensor comprising a plurality of sensing pads, at least one of the sensing pads of the plurality of sensing pads having a triangular shape, and the plurality of sensing pads are operable to detect a movement of a nearby controlling object prior to contact with the surgical robotic arm; and
a processor configured to determine a desired position of the surgical robotic arm based on the detected movement of the nearby controlling object and drive a movement of more than one of the plurality of robotic arm links or the plurality of j oints to achieve the desired position of the surgical robotic arm.
|
|
8. A control system for a surgical robotic arm, the control system comprising:
a sensor coupled to a surgical robotic arm and comprising a plurality of sensing pads arranged to form a circular sensing region and operable to detect a linear movement or an angular movement of a nearby controlling object prior to contact with a plurality of robotic arm links or a plurality of j oints of the surgical robotic arm; and
a processor configured to determine a desired position of the surgical robotic arm based on the detected movement of the nearby controlling object and drive a movement of more than one of the plurality of robotic arm links or the plurality of j oints to achieve the desired position of the surgical robotic arm.
|
|
15. A method for touch-free control of a surgical robotic arm based on proximity sensing, the method comprising:
receiving at least one sensor signal generated by a proximity sensor comprising a conductive material printed directly onto a surface of a surgical robotic arm, the at least one sensor signal corresponding to a movement of a nearby controlling object prior to contact with the surgical robotic arm, and the surgical robotic arm comprising a plurality of robotic arm links and a plurality of joints operable to move according to multiple degrees of freedom;
determining a desired position of the surgical robotic arm based on a detected movement of the nearby controlling object; and
controlling a movement of more than one of the plurality of robotic arm links or the plurality of joints to achieve the desired position of the surgical robotic arm.
|