| CPC H04W 28/0289 (2013.01) [H04L 47/193 (2013.01); H04L 47/27 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A method performed by an electronic device, for dynamically controlling a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) congestion window, comprising a modem, a communication processor (CP) being a lower layer of the modem, a TCP stack, and an application processor (AP) being a higher layer of the TCP stack, comprising:
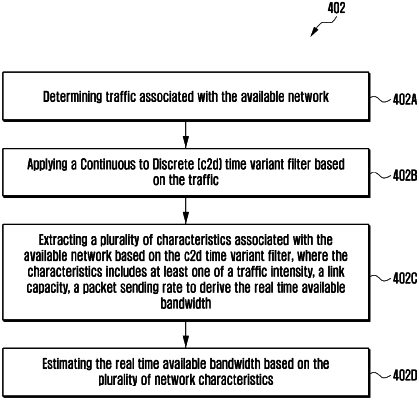
estimating a real time available bandwidth for an available network;
deriving a dynamic congestion window control factor from the estimated real time available bandwidth; and
modifying a congestion window based on the derived dynamic congestion window control factor,
wherein the congestion window is modified by passing information of the real time available bandwidth from the CP of the electronic device to the AP of the electronic device and adjusting the congestion window by the AP of the electronic device, and
wherein deriving the dynamic congestion window control factor from the estimated real time available bandwidth comprises:
estimating at least one of a size of a file to be uploaded, a quality of service, network conditions, or a priority based dynamic adaptation;
identifying an actual packet loss from a spurious packet loss based on at least one of the size of the file to be uploaded, the quality of service, the network conditions, or the priority based dynamic adaptation; and
deriving the dynamic congestion window control factor from the estimated real time available bandwidth based on the actual packet loss.
|