| CPC G16H 50/30 (2018.01) [G06F 40/205 (2020.01); G06F 40/30 (2020.01); G16H 10/60 (2018.01); G16H 15/00 (2018.01); G16H 30/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01)] | 17 Claims |
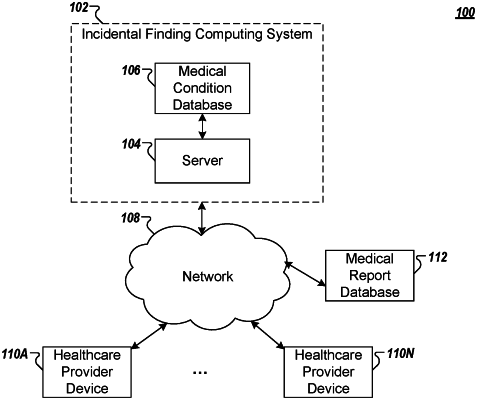
|
1. A computer-implemented method for identifying a condition of concern based at least in part on incidental medical findings, the method comprising:
receiving, by circuitry, a dataset output by natural language processing circuitry, wherein the natural language processing circuitry is configured to:
receive an electronic medical report, wherein the electronic medical report comprises a plurality of textual components and at least one non-textual component; and
perform natural language processing, wherein the natural language processing comprises:
(a) processing the plurality of textual components of the electronic medical report from natural language text to computer readable text by performing at least one of text normalization, tokenization, paraphrase and word variant recognition, acronym and abbreviation disambiguation, or document segmentation on the plurality of textual components,
(b) analyzing the computer readable text to derive a textual component of the plurality of textual components,
(c) identifying two or more medical findings from the derived textual component, wherein an electronic knowledge base is used to identify the two or more medical findings from the derived textual component,
(d) determining a context for each of the two or more medical findings, wherein each context comprises one or more modifiers or attributes for the corresponding medical finding and wherein determining the context for each of the two or more medical findings comprises determining one or more relationships between the two or more medical findings and associated anatomical regions, and
(e) outputting the dataset, wherein the dataset comprises each of the two or more medical findings and their respective corresponding contexts; and
performing, by the incidental finding circuitry, incidental medical finding processing, wherein the incidental medical finding processing comprises:
(a) receiving, by the incidental finding circuitry, the dataset comprising each of the two or more medical findings and their respective corresponding contexts output by the natural language processing circuitry,
(b) identifying, by the incidental finding circuitry, an excluded set of the two or more medical findings to exclude from further processing based at least in part on their respective corresponding contexts,
(c) identifying, by the incidental finding circuitry, an included set of the two or more medical findings to include for further processing based at least in part on their respective corresponding contexts, wherein the included set of the two or more medical findings comprises two or more incidental medical findings,
(d) querying, by the incidental finding circuitry, a database for one or more properties or one or more rules for identifying clinical cues associated with at least one of the two or more incidental medical findings of the included set of the two or more medical findings, for an associated condition of concern,
(e) identifying, by the incidental finding circuitry and based at least in part on the one or more properties or the one or more rules returned from the query, one or more clinical cues for each incidental medical finding of the two or more incidental medical findings of the included set of the two or more medical findings,
(f) determining, by the incidental finding circuitry and based at least in part on their respective corresponding contexts of the included set of the two or more medical findings, a gradient severity score for each of the one or more clinical cues, and
(g) determining, by the incidental finding circuitry and based at least in part on the respective gradient severity scores, a gradient risk level for a condition of concern corresponding to the one or more clinical cues, wherein (1) determining the gradient risk level for the condition of concern corresponding to the one or more clinical cues is in combination with one or more predefined risk levels, (2) a predefined risk level of the one or more predefined risk levels for the condition of concern is a medium risk level, and (3) the gradient risk level is adjusted based at least in part on the context of the clinical cues;
responsive to determining that the gradient risk level for the condition of concern corresponding to the one or more clinical cues satisfies one or more filter criteria, generating, by the circuitry, a condition alert indicating the condition of concern, wherein (1) the condition alert comprises at least one clinical cue satisfying at least one of the one or more filter criteria or the corresponding gradient severity score, and (2) generating the condition alert comprises at least one of (I) inserting a flag in an electronic medical record or (II) at least one of outputting an output indicator using a computer assisted coding application, providing a notification via a user interface, or outputting a medical report.
|