| CPC G06N 7/01 (2023.01) [E05B 15/0205 (2013.01); E05B 41/00 (2013.01); G06N 20/00 (2019.01); E05B 47/0001 (2013.01); E05B 2047/002 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0016 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0058 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0068 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0069 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0081 (2013.01); E05B 2047/0088 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
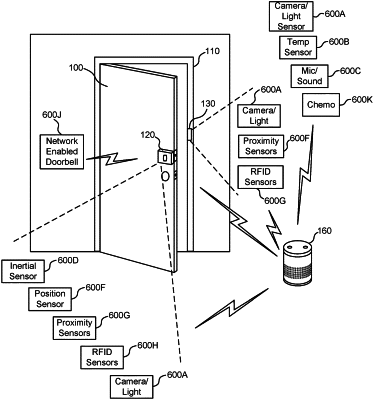
obtaining, from a plurality of sensing devices of different types, information indicating measurements of an environment associated with a door;
generating, based at least in part on the information, a set of inputs to a machine-learning model;
inputting the set of inputs into the machine learning model to determine a status indicating whether a lock associated with a physical access control mechanism of the door is engaged, wherein the machine learning model is trained using measurements of the environment associated with the door obtained from the plurality of sensing devices;
generating a message that indicates the status of the door; and
transmitting the message to a network address associated with the door.
|