| CPC G06N 3/08 (2013.01) [G06F 18/2413 (2023.01); G06F 18/2431 (2023.01); G06N 5/046 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method, comprising:
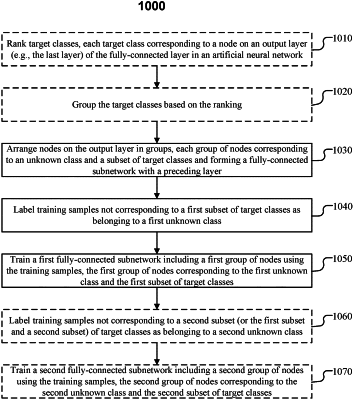
ranking target classes of an artificial neural network, the artificial neural network configured to classify objects into the target classes, each target class corresponding to a node on an output layer of a fully-connected layer in the artificial neural network;
grouping the target classes based on the ranking;
grouping the nodes on the output layer based on the grouping of the target classes, each group of nodes further comprising a respective node corresponding to a respective unknown class and forming a respective fully-connected subnetwork with nodes on an input layer of the fully-connected layer;
training each fully-connected subnetwork;
receiving a representation of an object to be classified;
classifying the object, using a first fully-connected subnetwork comprising a first group of nodes on the output layer, as a first unknown class instead of as a target class within a first group of target classes corresponding to the first group of nodes; and
as a result of classifying the object as the first unknown class, classifying the object, using a second fully-connected subnetwork comprising a second group of nodes on the output layer, as a target class within a second group of target classes corresponding to the second group of nodes or as a second unknown class;
wherein, if a particular object is classified as a target class within the first group of target classes, the second fully-connected subnetwork is not executed for classifying the particular object, wherein the first fully-connected subnetwork and the second fully-connected subnetwork share a same group of nodes on the input layer, and wherein the nodes on the input layer are directly connected to the nodes on the output layer.
|