| CPC G05B 13/041 (2013.01) [A01G 25/092 (2013.01); A01G 25/16 (2013.01); G05B 13/0265 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
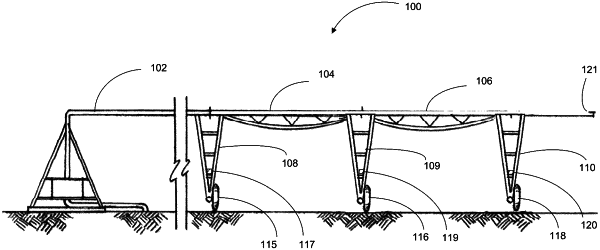
1. A system for use with a self-propelled irrigation system having at least one span and a drive system for moving the span across a field to be irrigated, the system comprising:
span mounted sensors, wherein at least one span mounted sensor comprises at least one sensor configured to allow for detection of crop data;
climate sensors, wherein at least one climate sensor is configured to detect at least one climate condition, wherein the climate condition comprises temperature; and
a machine learning module, wherein the machine learning module is configured to receive characteristic data for the field; wherein the machine learning module is configured to create a set of field objects for the field and use the characteristic data to create a predictive model for each defined field object based on the detected characteristic data for each field object within the field;
wherein the system of the present invention is configured to calculate an expected position (PE) of the drive tower after a given interval of time;
wherein the system is configured to detect the geo-location of the drive tower (P2) after the given interval of time;
wherein the system is configured to calculate a slip ratio based on a comparison between the estimated position (PE) and the detected position (P2); and
a processing module, wherein the processing module is configured to output a plurality of control signals to the drive system to adjust a first drive parameter based at least in part on the calculated slip ratio.
|