| CPC G01L 5/0052 (2013.01) [G01M 7/08 (2013.01); G01M 17/0078 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method comprising:
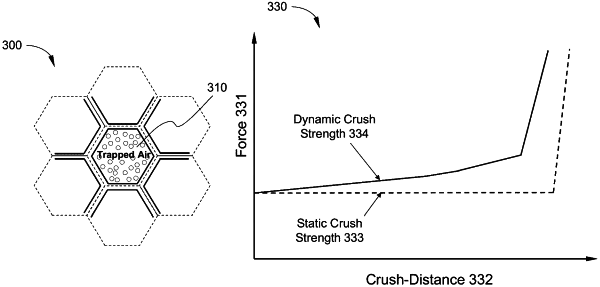
receiving a specification of a honeycomb based crash barrier including a plurality of cells with each of the plurality of cells containing trapped air;
generating a finite element analysis model representing the honeycomb based crash barrier using two-dimensional finite elements to represent the plurality of cells;
determining an air pressure of the trapped air versus crush-distance relationship for a cell of the plurality of cells based on a simulation of compressing the cell along a longitudinal axis of the cell according to a formulation characterizing a pressure, a density, and an internal energy of the trapped air;
transforming the air pressure of the trapped air versus crush-distance relationship for the cell into a force-deflection relationship for one-dimensional finite elements;
modifying the finite element analysis model to produce a modified model, the modified model including a compressible element for each of the plurality of cells, wherein each of the compressible elements comprise a one-dimensional finite element that behaves according to the force-deflection relationship;
simulating physical behaviors of the honeycomb based crash barrier using the modified model, the physical behaviors including numerical behaviors of the trapped air based on the force-deflection relationship and the one-dimensional finite elements; and
determining survivability of a human occupant in an automobile due to an impact event between the automobile and the honeycomb based crash barrier based on the simulated physical behaviors.
|