| CPC B64C 39/024 (2013.01) [G01C 21/005 (2013.01); G06V 10/44 (2022.01); G06V 20/17 (2022.01); G06V 20/176 (2022.01); G06V 20/64 (2022.01); B64U 10/13 (2023.01); B64U 2201/10 (2023.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
1. A method of vehicle operation for autonomous navigation of a flight path comprising:
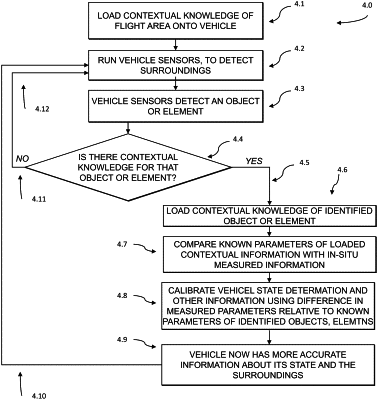
utilizing a vehicle comprising one or more onboard sensors and a local database, the local database storing pre-loaded data, the pre-loaded data comprising: object information for predetermined objects associated with a planned flight path;
the method further comprising:
using the one or more onboard sensors of the vehicle to scan a surrounding environment of the vehicle and detect an object in the surrounding environment;
matching the detected object in the surrounding environment to a predetermined object based on the object information from the pre-loaded data;
determining dimensions of the detected object by comparing an apparent size of the detected object as imaged by the one or more onboard sensors to a known size of the matched predetermined object based the object information from the pre-loaded data, wherein the determined dimensions of the detected object include dimensions of the detected object that are not detectable by the one or more onboard sensors;
calculating, based on the determined dimensions of the detected object, multiple flight routes for navigating the vehicle around the detected object and toward a target location along the flight path;
identifying, among the multiple calculated flight routes, a flight route having a shortest distance for navigating the vehicle around the detected object and toward the target location; and
controlling a vehicle control system of the vehicle to navigate the vehicle to travel to the target location along the identified flight route having the shortest distance.
|