| CPC B01L 3/50273 (2013.01) [B01L 3/502738 (2013.01); B01L 3/502746 (2013.01); B01L 2200/0605 (2013.01); B01L 2200/0621 (2013.01); B01L 2300/0861 (2013.01); B01L 2300/0867 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0433 (2013.01); B01L 2400/0442 (2013.01)] | 18 Claims |
|
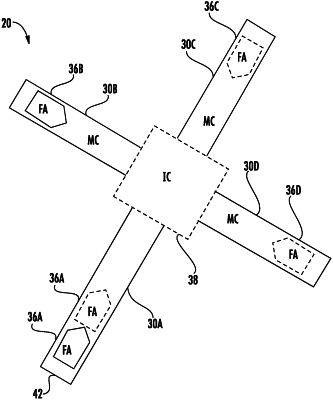
1. A microfluidic device comprising:
at least four interconnected microfluidic channels;
a set of fluid actuators comprising a fluid actuator asymmetrically located within at least two of the at least four interconnected microfluidic channels such that at least two of the at least four interconnected microfluidic channels may be activated to a fluid inputting state, a fluid outputting state and a fluid blocking state in response to selective actuation of different combinations of fluid actuators of the set, wherein the set of fluid actuators are activated at a same frequency and result in different flow rates of fluid within the interconnected microfluidic channels; and
one connecting channel extending between the first one of the at least four interconnected microfluidic channels to a second one of the at least four interconnected microfluidic channels wherein the one connecting channel is a passive channel lacking any fluid actuators.
|