| CPC A61N 1/36071 (2013.01) [A61N 1/048 (2013.01); A61N 1/0456 (2013.01); A61N 1/0556 (2013.01); A61N 1/20 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
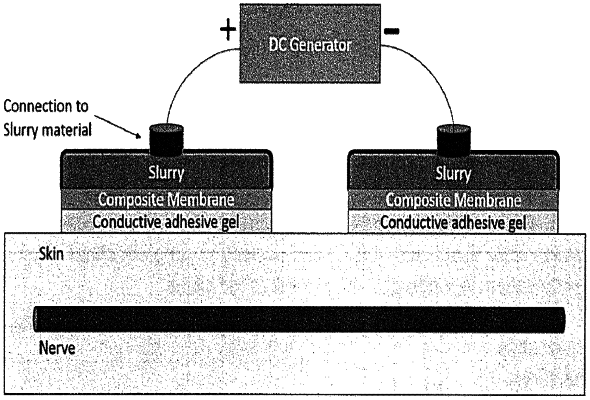
1. A method comprising:
placing a slurry electrode in proximity to neural tissue;
connecting the slurry electrode to a DC generator; and
applying a DC waveform generated by the DC generator to the neural tissue via the slurry electrode,
wherein the slurry electrode comprises a slurry of a plurality of electrically conducting high surface area particles each suspended in an ionically-conductive material and an ionically conductive membrane to prevent the slurry from contacting the neural tissue, wherein the slurry converts an electrical charge of the DC waveform to an ionic charge, and wherein the ionic charge is transmitted to the neural tissue through the ionically conductive membrane.
|