| CPC A61F 9/008 (2013.01) [A61B 90/98 (2016.02); A61F 9/009 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00477 (2013.01); A61B 2034/2051 (2016.02); A61F 2009/00846 (2013.01); A61F 2009/00855 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
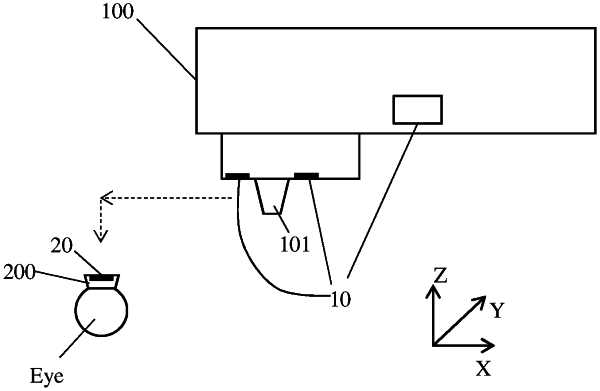
1. An ophthalmic surgical laser system comprising:
a laser delivery head, including optics which define an optical axis for delivering a laser beam to an eye of a patient;
a patient interface device having an RF (radio frequency) antenna configured to generate an RF signal;
three or more RF antennas affixed on the laser delivery head and located at defined locations in a plane perpendicular to the optical axis, each capable of measuring the RF signal generated by the RF antenna of the patient interface device, and
a control device electrically coupled to the three or more RF antennas and the laser delivery head, and configured to:
control each of the three or more RF antennas to measure the RF signal generated by the RF antenna of the patient interface device, and
based on comparisons of the measured RF signals from the three or more RF antennas, determine whether or not the patient interface device is located within a predetermined distance from the optical axis, and
based on comparisons of the measured RF signals from the three or more RF antennas, move the laser delivery head toward the patient interface device.
|