| CPC A61B 5/7282 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0022 (2013.01); A61B 5/08 (2013.01); A61B 5/4836 (2013.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 7/003 (2013.01); A61B 7/023 (2013.01); A61B 7/04 (2013.01); A61N 1/3601 (2013.01); A61N 1/3611 (2013.01); A61N 1/36514 (2013.01); A61B 2562/0219 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A system for managing a respiratory disease in a patient, the system comprising:
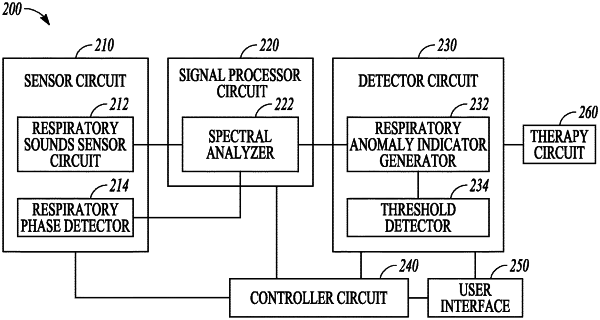
a sensor circuit including a sense amplifier coupled to at least one ambulatory or implantable physiological sensor to sense one or more physiological signals indicative of respiratory sounds, wherein the at least one ambulatory or implantable physiological sensor includes an accelerometer, and the one or more physiological signals include an acceleration signal sensed by the accelerometer;
a signal processor circuit including a spectral analyzer circuit configured to generate from the sensed one or more physiological signals a first spectral content of respiratory sounds within a first frequency band and a second spectral content of respiratory sounds within a second frequency band, the second frequency band having a higher center frequency than the first frequency band;
a detector circuit coupled to the signal processor circuit and configured to:
receive at least one physiological parameter of the patient different from the first and the second spectral contents, the received at least one physiological parameter including a blood pressure parameter;
calculate a correlation between (i) a change in at least one of the first spectral content or the second spectral content over time and (ii) a change in the received at least one physiological parameter including a change in the blood pressure parameter over time; and
generate a respiratory anomaly indicator using the calculated correlation, the respiratory anomaly indicator indicating a status of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or asthma of the patient; and
an output circuit configured to provide the respiratory anomaly indicator to a user or a process.
|