| CPC H01S 5/02326 (2021.01) [H01S 5/024 (2013.01); H01S 5/0231 (2021.01); H01S 5/0239 (2021.01); H01S 5/02212 (2013.01); H01S 5/02253 (2021.01); H01S 5/02251 (2021.01); H01S 5/02415 (2013.01); H01S 5/02469 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
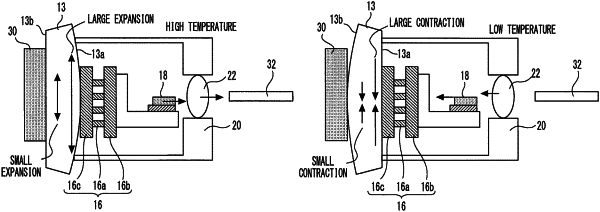
1. An optical module comprising:
a stem including a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface;
a thermoelectric cooler including a heat-releasing substrate fixed to the first surface;
a semiconductor laser element attached to the thermoelectric cooler;
a cap fixed to the first surface and covering the thermoelectric cooler and the semiconductor laser element;
a lens fixed to the cap; and
a restriction body fixed to the second surface, wherein
the linear thermal expansion coefficients of the heat-releasing substrate and the restriction body are smaller than the linear thermal expansion coefficient of the stem,
the semiconductor laser element is configured to emit light directly to the lens,
the linear thermal expansion coefficient of the restriction body is smaller than the linear thermal expansion coefficient of the heat-releasing substrate,
the stem is made of SPCC,
the heat-releasing substrate is made of aluminum nitride or alumina,
the restriction body is made of aluminum nitride or invar, and
the restriction body restricts thermal deformation of the second surface side of the stem such that positions of the laser element and the lens:
vary in a same first direction upon thermal expansion of the stem, and
vary in a same second direction opposite to the first direction upon thermal contraction of the stem.
|