| CPC G10L 21/028 (2013.01) [G10L 21/0208 (2013.01); G10L 25/84 (2013.01); G10L 2021/02087 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A signal processing device, comprising:
a central processing unit (CPU) configured to:
receive an input acoustic signal associated with a plurality of sound sources;
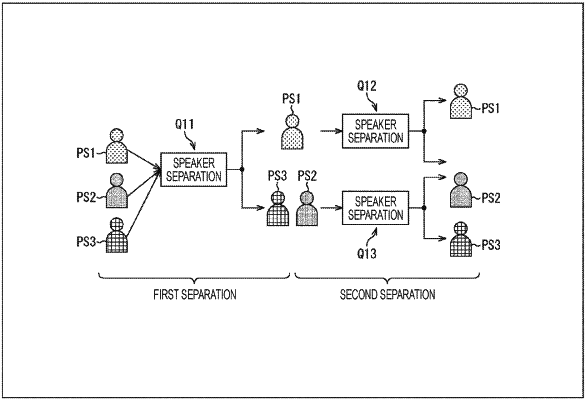
execute, based on a sound source separation model learned in advance to separate a sound source from an acoustic signal, a sound source separation on the received input acoustic signal;
generate, based on the sound source separation, a plurality of separated signals;
determine that the sound source separation on a separated signal of the plurality of separation signals is to be ended based on an end condition,
wherein the end condition is a condition that an average energy level of the separated signal of the plurality of separated signals is equal to or less than a specific threshold value;
execute the sound source separation on the plurality of separated signals that does not satisfy the end condition; and
recursively execute the sound source separation, on the plurality of separated signals that does not satisfy the end condition, until each of the plurality of separated signals satisfies the end condition,
wherein the sound source separation model is trained as a N-source model, and
a number of the plurality of sound sources is greater than N.
|