| CPC G06Q 10/107 (2013.01) [G06F 40/205 (2020.01); G06N 7/01 (2023.01); G06Q 30/018 (2013.01); G06Q 40/02 (2013.01); H04L 63/1416 (2013.01); H04L 63/1425 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
1. A computer-implemented method of detecting compromised digital electronic messages, the method comprising, executed by one or more business email compromise (BEC) detection computers:
receiving, from a digital electronic computer network, a digital electronic message that is directed to a recipient computer from a sender computer;
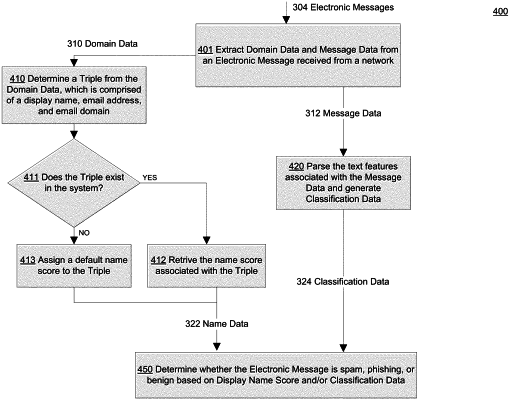
obtaining domain data and message data from the digital electronic message and storing the domain data and message data, the domain data comprising a triple identifier associated with the sender computer, the triple identifier being comprised of a display name, an email address, and an email domain associated with the sender computer, the message data comprising a plurality of text features;
comparing the triple identifier associated with the sender computer with one or more digitally stored triple identifiers in a domain database associated with the one or more BEC detection computers;
determining, in response to comparing the triple identifier with the one or more stored triple identifiers, a name score for the triple identifier indicating a probability that the digital electronic message associated with the sender computer is compromised;
parsing the plurality of text features of the message data;
inputting the plurality of text features of the message data into a plurality of classifiers, each classifier corresponding to a respective particular message type and having been machine-learned to determine a probability that a digital electronic message is associated with that respective particular message type;
determining, based on output of the plurality of classifiers, a message type of the digital electronic message; and
determining whether the digital electronic message is a BEC attack based on the name score for the triple identifier associated with the sender computer and the message type of the digital electronic message.
|