| CPC G05D 3/20 (2013.01) | 10 Claims |
|
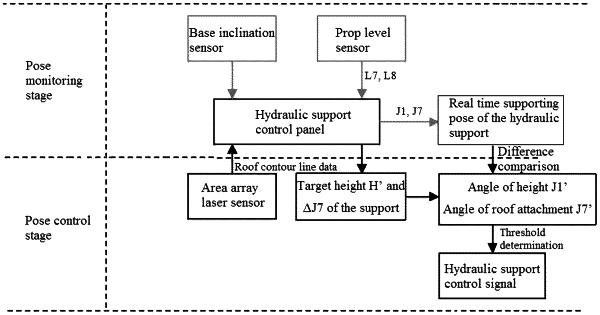
1. A monitoring and controlling method for a supporting pose of a supporting type hydraulic support, comprising:
A. support pose monitoring process:
a1. by using a prop level sensor of the hydraulic support, reading length parameters of a front prop and a rear prop;
a2. in combination with a relationship of length parameter and angle parameter of the support, establishing a pose monitoring mathematic model;
a3. based on an interpolation algorithm, solving equilibrium equations of the pose monitoring mathematic model to obtain pose parameters comprising associated pose parameters of an angle of height, an angle of roof attachment, an angle of inclination of the front prop and an angle of inclination of the rear prop;
B. support pose control process:
b1. based on the parameters obtained in the support pose monitoring process, determining a current supporting pose;
b2. by using an area array laser sensor, obtaining a contour line of a roof above the support, and determining a bulging edge of the roof;
b3. obtaining a height difference between a support canopy and the roof, and establishing a height difference calculation mathematic model;
b4. based on the height difference calculation mathematic model, calculating a target height and a target angle of roof attachment of the hydraulic support;
b5. establishing a target angle-of-height calculation mathematic model, and determining, by calculation, a target angle of height of the support;
b6. substituting the parameters of the target angle of height and the target angle of roof attachment into the pose monitoring mathematic model and by the interpolation algorithm, solving target lengths of the front prop and the rear prop;
wherein the control panel outputs a proportional control signal, based on the solved target lengths, to adjust the support pose.
|