| CPC C07K 9/001 (2013.01) [A61K 9/5123 (2013.01); A61K 9/5169 (2013.01); A61K 9/5192 (2013.01); C07K 16/2818 (2013.01); B82Y 5/00 (2013.01)] | 40 Claims |
|
1. A compound of formula (I):
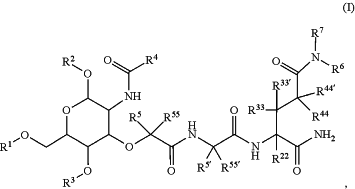 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof,
wherein:
R1 is —H or —C(O)—RX;
R2 and R3 are each independently selected from the group consisting of —H, alkyl, aryl, alkylene-aryl, —C(O)-alkyl, and —C(O)-aryl;
R4, R5, and R5′ are each alkyl;
R6 and R11 are each independently —H or alkyl;
R7 is —Y-triazolyl-L;
Y is alkylene;
L is selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid chain, -alkylene-C(O)—W, -alkylene-O—C(O)—W, -alkylene-N-(alkylene-C(O)—NR11-alkylene-NR11—C(O)—W)2, and -alkylene-N-(alkylene-C(O)—W)2;
W is a fatty acid chain, —O-alkylene-C(H)(OR8)-alkylene-OR9, a phospholipid, or a sterol;
R8 and R9 are each independently RX or —C(O)—RX;
R22, R33, R33′, R44, R44′, R55, and R55′ are each independently H or RA;
RX is a fatty acid chain;
wherein each aforementioned alkyl, alkylene, alkylene-aryl, aryl, and triazolyl is optionally substituted with one or more RA, wherein RA is independently selected for each occurrence from the group consisting of hydrogen, halo, alkoxy, haloalkoxy, cyano, hydroxyl, —N(RC)(RD), —C(O)N(RC)(RD), —N(RC)C(O)RB, —OC(O)NRCRD, —NRCC(O)ORB, —OC(O)RB, —C(O)ORB, —C(O)RB, —CO2H, —NO2, —SH, S(O)XRB, aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl, heteroarylalkyl, cycloalkyl, heterocycloalkyl, and RB; wherein X is 0, 1, or 2,
RC and RD are independently selected for each occurrence from the group consisting of hydrogen, alkyl, haloalkyl —C(O)RB, and —C(O)ORB; or RC and RD are taken together with the nitrogen to which they are attached to form a heterocyclic ring optionally substituted with RA; and
RB is alkyl, alkenyl, or alkynyl optionally substituted with one or more fluoro.
|