| CPC A61B 6/12 (2013.01) [A61B 6/03 (2013.01); A61B 6/4441 (2013.01); A61B 6/463 (2013.01); A61B 6/504 (2013.01); A61B 6/5235 (2013.01); G06T 7/30 (2017.01); A61B 6/4458 (2013.01); A61B 6/481 (2013.01); A61B 6/487 (2013.01); A61B 6/5223 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. An angiographic examination method for depicting a target region inside a patient with a vascular system as an examination object using an angiography system comprising an X-ray emitter and an X-ray image detector that are attached to ends of a C-arm, a patient positioning couch with a tabletop on which the patient is positioned, a processor, an image system, and a monitor, the angiographic examination method comprising:
capturing a volume data set of the target region with the examination object;
registering the volume data set to the C-arm;
extracting information about an assumed course of vessels of the examination object in the volume data set inside the target region;
generating at least one two-dimensional (2D) projection image of a medical instrument inserted in the target region;
generating a 2D overlay image, the generating of the 2D overlay image comprising 2D/three-dimensional (3D) merging of the at least one 2D projection image and the registered volume data set;
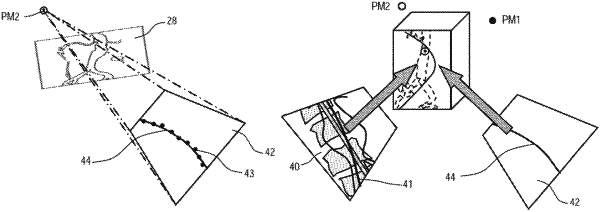
detecting the medical instrument inserted in the target region in the 2D overlay image with a first projection matrix;
generating a virtual 2D projection of the medical instrument using a virtual projection matrix, wherein the virtual projection matrix is based on the first projection matrix, and wherein generating the virtual 2D projection of the medical instrument comprises:
generating the virtual projection matrix, the generating of the virtual projection matrix comprising rotating the first projection matrix by an angle about an axis through the patient;
generating the virtual 2D projection of the medical instrument using the virtual projection matrix; and
approximating the medical instrument in the virtual 2D projection of the medical instrument, the approximating comprising estimating the position of the medical instrument from the virtual 2D projection of the medical instrument;
reconstructing the medical instrument in three dimensions, in which a 3D position of the medical instrument is determined based on the virtual 2D projection and the detected medical instrument in the 2D overlay image; and
overlaying a reference image that shows a status of the target region before the insertion of the medical instrument, and the reconstructed medical instrument, the determined 3D position of the medical instrument, or the reconstructed medical instrument and the determined 3D position of the medical instrument, and displacing at least a part of the reference image such that a current course and the assumed course of the vessels are congruent.
|